
Why the next Windows 11 update is skipping Intel and AMD
Microsoft’s upcoming Windows 11 26H1 update is rolling out only to devices powered by Snapdragon chips, at least for now. While it might seem like

Microsoft’s upcoming Windows 11 26H1 update is rolling out only to devices powered by Snapdragon chips, at least for now. While it might seem like

Microsoft is pushing the boundaries of AI with an experimental feature in Windows 11 called the Agent Workspace. This new tool allows AI agents to
You didn’t start a business to spend your evenings renaming files or copy-pasting numbers from PDF invoices. Yet, for many small-business owners, these repetitive administrative

Wish your laptop could last longer on a single charge? Big changes could be on the way that help your team work smarter (and stress less about finding outlets).
Learn more about this business-boosting improvement from Microsoft and Windows 11.

Wish your laptop could last longer on a single charge? Big changes could be on the way that help your team work smarter (and stress less about finding outlets).
Learn more about this business-boosting improvement from Microsoft and Windows 11.

Every October, Cybersecurity Awareness Month highlights one essential truth: digital threats are real, but so is resilience.

Windows 11’s latest features demand a solid foundation. However, simply upgrading from an older version of Windows can drag old problems into a new system.

Wish your laptop could last longer on a single charge? Big changes could be on the way that help your team work smarter (and stress less about finding outlets).
Learn more about this business-boosting improvement from Microsoft and Windows 11.

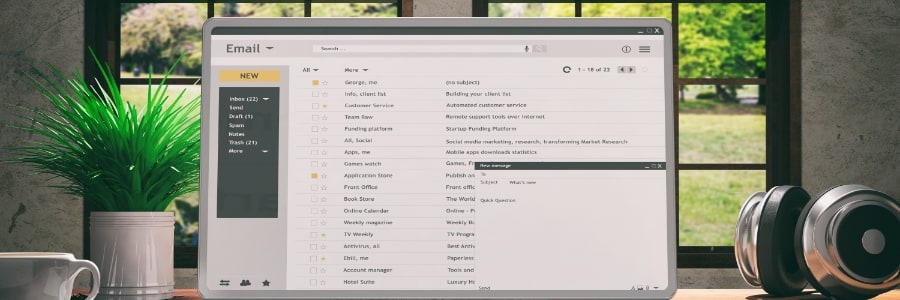
Your inbox is about to get a powerful new ally. Find out how Outlook’s latest feature could help you cut through the noise of junk and spot the emails that really matter (and save time too).

Do you know who in your business can access your critical data right now?
The risks that come along with that can be bigger than you think. Our latest tech update explains why this matters and what smart businesses are doing about it